Table of Contents
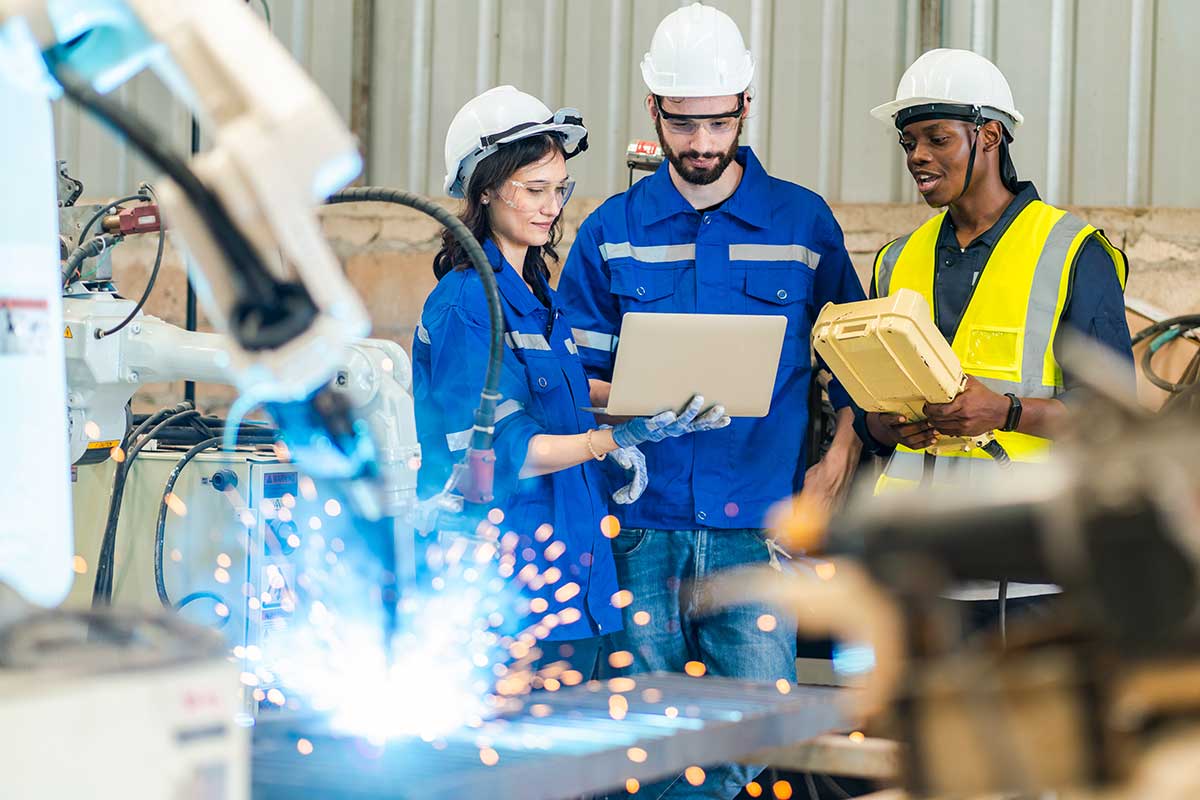
Modern manufacturing is at a crossroads. As factories evolve into smart, interconnected hubs, the need for seamless and reliable communication systems has never been more critical. Advanced tools like Private 5G, Io, and push-to-talk (PTT) technology are no longer optional; they are. essential for maintaining competitive edge and operational efficiency.
This report explores how modern communication systems support manufacturing and leads to smart factories. It covers the latest technologies and highlights how Galaxy Broadband ensures 99.9% uptime.
This report examines how these modern communication systems support and transform manufacturing, ensuring continuous connectivity and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Modern manufacturing relies on advanced communication systems for smart factories.
- Private 5G and IoT are critical for connectivity and efficiency.
- Push-to-talk (PTT) phones enhance internal communication in manufacturing plants.
- Communication systems enable predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and safety.
- Industry 4.0 technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics boost productivity and data-driven decisions.
- Private 5G networks provide secure, high-speed, and uninterrupted connectivity.
- LEO satellites ensure global connectivity, crucial for remote construction sites.
- Combining Private 5G and LEO satellites achieves 99.9% uptime.
- Challenges include financial constraints, skill gaps, and technological complexity.
- Galaxy Broadband offers flexible, reliable, and scalable connectivity solutions.
- Future technologies like 6G and edge computing will further enhance manufacturing.
Overview of Modern Communication Systems in Manufacturing
Manufacturing has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Traditional assembly lines have transformed into smart factories, where machines, sensors, and humans work together seamlessly. This transformation relies on advanced communication systems that ensure real-time data exchange and coordination.
Definition and Scope
To understand how these systems work, let’s start by defining what modern communication systems in manufacturing entail.
Modern communication systems in manufacturing include various technologies designed to facilitate efficient and reliable information flow. These systems include wired and wireless networks, communication protocols, push-to-talk (PTT) technology , push-to-video (PTV), and devices that enable connectivity among machines, control systems, and workers.
Evolution Over the Years
Now that we have a clear definition, it is helpful to examine how these systems have evolved over the years.
In the past, manufacturing relied heavily on wired communication systems, which, while reliable, had limitations regarding flexibility and scalability. With the introduction of wireless technologies, particularly Wi-Fi and cellular networks, manufacturers began to experience greater mobility and easier installation. However, these early wireless systems often struggled with interference and reliability issues.
The real game-changer came with the development of Industry 4.0, which integrates cyber-physical systems, IoT, and cloud computing into manufacturing. Industry 4.0 requires robust communication systems capable of handling vast amounts of data with low latency and high reliability. This is where technologies like Private 5G and LEO solutions come into play, offering speed, security, and reliability.
This historical perspective highlights how crucial communication systems have become in today’s manufacturing landscape.
Importance in Today’s Manufacturing
Communication systems are the backbone of operational efficiency in modern manufacturing. Tools like push-to-talk (PTT) and push-to-video (PTV) technology enable instant communication, supporting predictive maintenance by allowing machines to communicate their status and performance data. They support remote monitoring and control, essential for managing distributed manufacturing sites. Additionally, they enhance safety by enabling real-time alerts and coordination during emergencies
Manufacturers now require continuous, reliable connectivity systems to ensure production lines run smoothly and minimize downtime. This need for reliability and efficiency drives the adoption of cutting-edge communication technologies, which support current manufacturing processes and pave the way for future innovations.
Adopting advanced communication systems can also contribute to sustainability efforts. For example, predictive maintenance reduces waste and energy consumption by ensuring machines operate efficiently. Additionally, remote monitoring and control can minimize the need for physical travel, reducing the carbon footprint.
As we explore this report further, we’ll explore specific technologies enhancing manufacturing communication, starting with Private 5G and IoT, and examine how they contribute to creating a more connected and efficient manufacturing environment.
The Role of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 represents the integration of digital technologies with manufacturing processes. This evolution is as critical as implementing lean strategies—companies risk being left behind without it.
The core technologies behind it include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): This technology connects devices for real-time data exchange. Its integration enables smarter operations by supporting predictive maintenance, quality control, and efficient resource management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enhances decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Additive Manufacturing: Enables rapid prototyping and complex designs.
- Robotics: Automates repetitive tasks for increased precision and efficiency.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): Assists in training and complex assembly tasks.
These Industry 4.0 technologies can boost factory productivity by 10–25% , adding 1–1.5% to a nation’s annual productivity growth.
With these technologies in place, let’s examine their tangible impacts on manufacturing processes.
Impact on Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 significantly enhances manufacturing by improving communication and integrating advanced technologies. Here’s the various ways it benefits manufacturing processes:
- Enhanced Connectivity: Machines, sensors, and systems communicate in real-time, improving coordination and speeding up decision-making.
- Increased Automation: Robots and automated systems take over repetitive tasks, boosting productivity and reducing errors.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Factories generate massive amounts of data. Advanced analytics convert this data into actionable insights, optimizing processes and reducing waste.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors continuously monitor machine health, predicting failures before they happen and minimizing downtime.
- Flexible Production: Factories can quickly switch production lines to different products, reducing changeover time and enhancing responsiveness to market demands.
To illustrate, IoT applications in manufacturing are expected to generate $1.2–$3.7 trillion in global economic value annually by 2025.
Why Advanced Communication Systems Matter in Industry 4.0
Robust communication networks are crucial for enabling Industry 4.0 capabilities. They enable the automation and seamless integration of various technologies in manufacturing.
Private 5G Networks
Additional benefits include heightened security, as data is kept within the private network, and the ability to support advanced applications such as augmented reality (AR) for maintenance, push-to-talk (PTT) or push-to-video (PTV) for quick communication, and remote assistance, further boosting productivity and innovation in manufacturing processes.
Adopting a private 5G network means factories gain complete control over their connectivity infrastructure. They can customize network configurations to meet specific operational needs, ensuring optimal performance.
Private 5G networks also minimize interference from external sources, leading to maximized uptime and enhanced reliability. This uninterrupted connectivity is required to maintain continuous production and improve operational efficiency.
Additional benefits include heightened security, as data is kept within the private network, and the ability to support advanced applications such as augmented reality (AR) for maintenance and remote assistance, further boosting productivity and innovation in manufacturing processes.
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites
In addition to Private 5G, another key technology is Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites. These satellites, such as those provided through Galaxy Broadband’s partnership with Eutelsat OneWeb , provide low-latency communication for real-time data exchange and remote monitoring, maintaining synchronized operations across locations.
These satellites offer low-latency communication, essential for real-time data exchange and remote monitoring. They help maintain synchronized operations across different locations.
LEO satellite networks can scale easily to meet growing data demands, making them a flexible solution for expanding manufacturing operations.
Combining Private 5G and LEO Satellites
Combining Private 5G and LEO satellite connectivity offers a comprehensive solution for manufacturing operations, ensuring robust, high-speed, and low-latency communication within and across remote sites. This dual approach provides a failover mechanism critical for maintaining continuous operations and achieving 99.99% uptime.
A prime example of the power of this combination is the Gahcho Kué Mine, a joint venture between De Beers Group and Mountain Province Diamonds in Canada’s Northwest Territories. Galaxy Broadband implemented a dual connectivity solution involving Private 5G and LEO satellite networks . This technological leap supports various applications, from autonomous hauling to real-time equipment monitoring.
The primary aim was to replace outdated communication systems with a robust, low-latency network capable of handling high-capacity data in a secure environment. This was particularly challenging given the mine’s remote location. The new network now serves as the backbone for other technological solutions at the mine, including Intelligent Edge computing systems and various sensor technologies.
Image: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AyhIJS8uf86lIX4vTrjx2cH-HsiaNZW5/view?usp=sharing
Alt Text: Industrial worker in high-visibility gear inspecting a metal component in a factory setting, using push-to-video (PTV) technology on a smartphone.
Push-to-Talk (PTT) and Push-to-Video (PTV) Technology
Push-to-talk (PTT) and push-to-video (PTV) technology remains a critical foundation for manufacturing communications. Designed for use in harsh and industrial environments, modern industrial handhelds are both durable and reliable, often meeting IP68 and MIL-810H ratings. They are intuitive to use and easy to operate in the field even while wearing gloves, thanks to a clear display, oversized programmable keys, and a range of ruggedized accessories.
These devices support push-to-talk, push-to-video, and other business-critical applications. When used with team communication software, workers can speak and stream video to one colleague or many. They support a wide range of 4G/LTE and 5G bands for reliable operation around the globe.
PTT and PTV technology enhances employees’ ability to collaborate and act on real-time information. These devices provide better coverage and clearer voice communication, essential for noisy environments with internal barriers and obstructions. Wireless accessories and noise-canceling headsets enable plant workers to interact freely while protecting their hearing.
Modern industrial handhelds integrate voice, data, text messaging, and GPS to help resolve equipment issues and reduce unplanned downtime faster. They interconnect personnel and equipment to streamline production, automate processes, manage risk, and respond to customers quickly. This makes PTT and PTV technology a cornerstone of inte grated plant communications, ensuring safety and operational efficiency.
Challenges and Adoption
Adopting Industry 4.0 involves significant challenges. Despite its potential, only about 10% of companies in key sectors —automotive, consumer goods, electronics, industrial equipment, engineering, and process industries—have fully embraced the strategic, operational, and cultural changes required for Industry 4.0. These pioneers are leading the way in manufacturing innovation, but many others lag due to several hurdles.
Financial Constraints
Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies requires substantial investment. The costs of new machinery, IoT devices, advanced software, and robust communication networks can be prohibitive. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often struggle to secure the necessary funding. Even larger companies may face budget limitations, making allocating resources for these extensive upgrades challenging.
Lack of Knowledge and Skills
A significant barrier to adopting Industry 4.0 is the workforce’s lack of knowledge and skills. These new technologies require specialized expertise that many current employees lack.
There is a need for more trained professionals who understand the complexities of IoT, AI, robotics, and advanced analytics. Companies must invest in training and development programs to upskill their workforce, which takes time and resources.
Additionally, the rapid pace of technological advancements can make it difficult for employees to keep up with the latest trends and tools.
Complexity of New Technologies
The complexity of Industry 4.0 technologies can be daunting. Integrating various systems—IoT devices, AI, and robotics—into existing manufacturing processes requires careful planning and execution.
Companies must ensure compatibility between new and legacy systems, which can be technically challenging. Moreover, transitioning to a digital factory involves significant changes to workflows and business processes.
Managing these changes effectively is crucial to avoid disruptions in production.
Enhanced Connectivity Management Through Galaxy Broadband
Galaxy Broadband’s advanced connectivity management is a critical enabler for companies adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. Their services offer flexible and scalable site connectivity options, ensuring reliable packet delivery and guaranteed committed information rate (CIR). This can serve as the primary connection for unserved sites or as a backup solution to enhance site resilience, providing continuous and dependable communication.
Galaxy’s services support various customer applications, including enterprise primary and backup, cloud migrations, critical communications, community aggregation, and cellular backhaul.
Galaxy’s solutions provide low latency, high-speed connectivity, and fiber-like performance, which is essential for real-time applications and cloud architectures.
Seamless Coverage and Easy Deployment
Galaxy Broadband provides 100% global coverage and offers easy deployment across Canada.
Its solutions are supported by a ground network in Canada and a 24/7 customer care center. Quick and flexible hardware installation and implementation support ensure seamless integration into any site.
Additionally, Galaxy’s team includes a skilled workforce that is well-versed in the latest technologies, ensuring that all installations and configurations are performed to the highest standards.
Innovative Network Technology
Galaxy is deploying cutting-edge Private 5G solutions in partnership with Nokia across diverse industries. These networks offer robust, reliable, and secure low-latency connectivity, transforming operations at remote sites across Canada.
In addition to Private 5G, Galaxy offers Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and Geostationary Orbit (GEO) satellite networks, ideal for remote sites where traditional connectivity options are unavailable. LEO and GEO networks provide high-speed, low-latency communication crucial for real-time data exchange and remote monitoring.
Galaxy Broadband’s fibre optic solutions deliver unparalleled speed and reliability for businesses in urban and suburban areas, supporting extensive data requirements and critical applications.
The Future of Manufacturing Connectivity
As manufacturing continues to evolve with Industry 4.0 technologies, the importance of robust communication systems cannot be overstated. Advanced solutions like Private 5G and LEO satellites are enhancing current operations and paving the way for future innovations.
Technologies like 6G , edge computing, and quantum communication are set to revolutionize manufacturing further. These advancements promise even faster data transmission, lower latency, and enhanced security, opening up new possibilities for smart factories.
Adopting these advanced communication technologies is crucial to staying ahead in the manufacturing landscape. Start by assessing your current communication infrastructure, investing in necessary upgrades, and training your workforce. Partner with industry leaders like Galaxy Broadband to ensure your operations remain connected, efficient, and competitive.